Update: The ISO 27001:2013 framework has been updated to ISO 27001:2022, and we’ve dedicated an entire blog post to provide you with a detailed overview. For an in-depth understanding of these changes and their implications, we invite you to read our latest article linked here.
If you’re selling to global companies, you’re likely getting questions about whether you adhere to ISO 27001. This information security framework was designed to be an international standard for businesses to use to protect the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of information in organizations of various sizes and industries.
ISO 27001 is most often used by international organizations to establish and audit their information security management, or to evaluate risks associated with third-party vendors. The set of standards was developed by two major organizations, ISO and IEC (respectively, the International Organization for Standardization and the International Electrotechnical Commission).
Here’s the basics you need to know about ISO 27001, how to know if it is right for your business, and how to get started implementing this security framework.
What is ISO 27001?
Formally known as ISO/IEC 27001, it is a part of the leading international standards for information security. It was published by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) in 2013 in partnership with the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC). The framework was revised in 2019.
ISO 27001 emphasizes the adoption of an Information Security Management System (ISMS). This approach is intended to merge information security with a cohesive management system to provide a cohesive set of controls – something that many fast-growing businesses may initially lack.
ISO 27001 looks at traditionally non-IT assets, which can make this particular standard seem more approachable to many organizations.
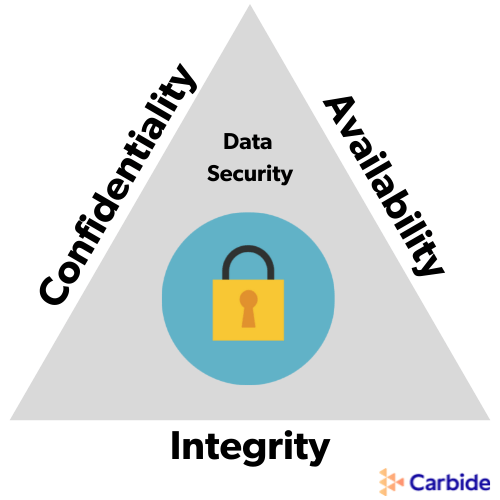
Confidentiality, Integrity, Availability
An ISMS is a set of rules that a company establishes to assess, manage, and mitigate risks in relation to their information security. These are often articulated as a set of security objectives. In ISO 27001, the security objective lies in protecting three aspects of information:
- Confidentiality: Through a series of robust access controls, only the right people will have the right access to data.
- Integrity: Control is tightened by limiting the ability to alter or destroy information.
- Availability. All data must be available to authorized individuals whenever it’s needed.
Together, these are known as the C-I-A triad.
Getting Started Implementing ISO 27001
ISO 27001 is a robust and detailed standard which is available for purchase (unlike CIS Controls or the NIST Cybersecurity Framework, which are available for free). Achieving ISO 27001 requires certification with an accredited registrar, and that cost will vary according to your organization’s size and the scope of compliance (similar to a SOC 2 audit).
To get started towards compliance with ISO 27001 and prepare for certification, there are a number of actions you can start taking immediately.
1. Gather the Mandatory Documents, Starting with Your Policies
ISO 27001 is unique in that it requires a list of mandatory documented policies, procedures, plans, and records that must be present during your audit to receive certification. For nearly any security framework, establishing a robust set of policies is your first step. These are some of the policies and documents you’ll need:
- Information Security Policy
- Risk Assessment, plus Risk Treatment Plan and methodologies
- Statement of Applicability
- Definitions of security roles and responsibilities
- An inventory of business assets
- Acceptable Use of Assets Policy
- Access Control Policy
- IT Management Operating Procedures
- Secure System Engineering Principles
- Supplier Security Policy
- Incident Response and Management Plans
- Business Continuity Plan
- Mandatory compliance requirements
In addition, your auditor will ask you for a series of records. These prove that your security policies are actively maintained. You’ll need to show:
- Records of training, skills, and qualifications
- Monitoring and measurement results
- Internal audit programs and their results
- Results of corrective actions
- Logs of user activities, anomalies, and security events
2. Perform a Risk Assessment
Risk management forms the core of the ISMS for ISO 27001. At this point, it’s a good idea to create a task force to handle the risk assessment. Alternatively, you may wish to bring third-party professionals on board to ensure that you conduct a thorough risk assessment and treatment process.
If you want the essentials about this topic, we have a blog post on risk assessment here. And a short video you can check out on risk assessments as well.
3. Address Each Identified Risk Using the Five Classes of Controls
Once you’ve identified potential risks and vulnerabilities, you’ll need to address each of them. ISO 27001 lays out five types of controls that a solid information security program includes. These are:
- Technical controls. Make sure your information systems involve backup solutions, antivirus or endpoint protection software, firewalls, patch management, configuration management and other infrastructural controls.
- Organizational controls. These include acceptable use policies, user permissions, roles within identity and access management, organizational structures, approvals and clear definitions of responsibility for all personnel.
- Legal controls. These include non-disclosure agreements, service level agreements, data ownership agreements, contracts, and mandatory compliance requirements or other laws to which the company is subject.
- Physical controls. Equipment or devices that help to manage physical access control or security should be implemented and documented. These include alarm systems, locks, access codes, and more.
- Human resource controls. ISO 27001 requires several human resource controls, such as security awareness training, internal auditor training, or other means to enhance employees’ knowledge of information security.
4. Satisfy the Requirements for ISO 27001
Finally, besides all the above, ISO 27001 defines a series of mandatory requirements that must be implemented for an organization to attain compliance. They are identified in Clauses 4 through 10 in the manual. The seven requirement sections include:
- Clause 4: Context of the organization. Defines the ISMS scope, the contexts for external and internal issues, plus interested parties and the requirements they’ve introduced.
- Clause 5: Leadership. Top management responsibilities should be clearly identified, informing the contents of the top-level Information Security Policy.
- Clause 6: Planning. Here, the exact requirements are defined for your risk assessment and treatment, statement of applicability, and other information security objectives.
- Clause 7: Support. You’ll need to identify resources, competencies, communication requirements, and the control of documents or records gathered for ISO 27001.
- Clause 8: Operation. This clause defines how procedures and policies are implemented, as well as processes that are needed to achieve your information security objectives.
- Clause 9: Performance evaluation. You’ll find the requirements for clearly defined monitoring, measurement, analyses, audits, and management review processes.
- Clause 10: Improvement. Includes the requirements for handling improvements to your policies arising from nonconformities, corrections, or continual improvement.
Start Pursuing ISO 27001 Compliance Today with Carbide
Using an information security management platform can get you started quickly, with expert guidance, and stay organized as you move through the mountain of requirements for implementing ISO 27001. By putting all your policies, processes, and procedures in one place, you’ll see can start checking off compliance requirements and gain a clear picture of what you need to do next.
Hopefully, we’ve given you a good sense of what goes into achieving compliance with ISO 27001. It is a great choice for organizations that need a robust security program, especially to satisfy international clients. This robust, risk management-oriented approach to information security is known for its comprehensiveness.
Looking to get started toward ISO 27001 certification? Your first step is getting the right policies in place to lay a solid foundation. Talk with our team to learn how the Carbide Platform can help automate your information security compliance program.